The Cutting Edge of Medical Technology Content, Community & Collaboration
The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) is a process control system that is aimed at identifying the points or areas at which hazards (dangers) may arise in the food chain. It prescribes strict measures for manufacturers and transporters of food products to prevent contamination and the resultant hazards. Control of hazards in the food chain has always been a need, but HACCP assumes added significance in today’s world, where globalization has made it possible for food to travel to hitherto unexplored parts of the world.
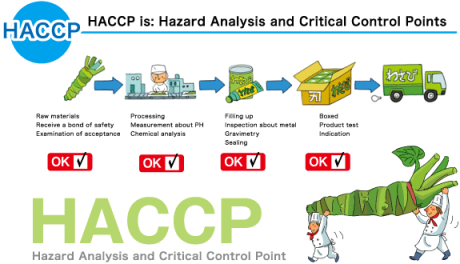
While this development has increased the choices before the consumers of food; it also brings challenges in the form of having to maintain hygiene and cleanliness standards throughout the often long food chains, usually over long periods of time. HACCP is considered a path breaking system in that it looks at food hazards very holistically and comprehensively. It seeks to control the onslaught of major microbiological contaminants in food such as E.coli, salmonella, listeria and many others that could cause diseases.
Tackling contamination from all sources
HACCP adapts a comprehensive view of all the sources of contamination, and seeks to prevent risks to food from all sources, such as:
- Microbiological
- Chemical
- Physical
In addition, it also prescribes steps aimed at putting in place a hazard control system that consists of seven important steps:
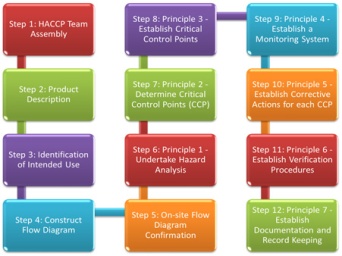
- Conducting a hazard analysis for identifying potential hazards that could enter the food production process
- Identifying the critical control points (CCPs), which are points in the process in which the potential hazards could occur and taking steps to prevent and control them
- Establishing critical limits for preventive measures associated with each CCP
- Establishing CCP monitoring requirements to ensure that each CCP stays within its limit
- Establishing corrective actions where monitoring shows that a CCP is not within the established limits. The aim of the corrective actions is to prevent public health hazards from occurring
- Establishing effective recordkeeping and documenting procedures to ensure that the HACCP system is working rightly. Documentation should show the ways in which CCPs are being monitored, as well as verification activities and deviation records
- Establishing procedures for verifying that the entire HACCP system is working and offering the desired outcomes.
Good intentions not backed by validation requirements
The noble intentions behind the HACCP systems and the stringent and serious endeavors towards their implementation notwithstanding; one grouse that food experts have had of the HACCP till recently is that the validation aspect of these hazards has not been given the same importance as other factors. Validation has no doubt been a part of HACCP, but somehow, it has been sort of overshadowed by the emphasis on verification.
It is only of late that validation has been gaining in prominence as a control measure. Companies need to validate their products by properly designing and taking adequate control measures that are capable of controlling food hazards within the process.
Understanding the role of validation in HACCP
A valuable learning session that will emphasize the importance of validation in the HACCP system is being organized by Compliance4All, a leading provider of professional trainings for all the areas of regulatory compliance.
Ruth Bell, a Food Safety/Quality and HACCP Management Consultant, Auditor and Trainer, who has worked on a number of projects helping organizations throughout the food chain to design, develop, implement and verify manageable food safety systems tailored to their needs, is the speaker at this webinar. Ruth is well known for her practical Quality and HACCP knowledge as an auditor, consultant and trainer. Please register for this webinar by visiting Food Safety Control Measures
Putting in place scientific validation measures
The aim of this session is to drive home the importance of validating food safety control measures to ensure food safety management system capability. Validation of food safety control measures is an essential measure in ensuring that a food safety management system will be capable of producing safe food and remains effective over a period of time.
Validating food safety control measures requires a theoretical examination of the scientific justifications for the control measures identified and practically challenging them to determine they will be suitable and capable of consistently achieving the required level of control to ensure safe food. Ruth will dwell on these aspects in detail at this webinar.
This webinar is aimed at HACCP team members and leaders, technical/quality managers, food safety managers, as well as auditors of food safety and HACCP systems, and specifically for specialists in positions such as HACCP Team Members, Technical Managers, Production Managers, Engineering Managers, and Consultants.
The speaker will cover the following areas at this webinar:
- Current Guidelines for Validation
- Differences between Verification and Validation Activities
- Components of Food Safety Management System Validation
- Validation Techniques including SPC, Predictive Microbiological Methods, and Challenge Testing.
Views: 17
Comment
© 2025 Created by CC-Conrad Clyburn-MedForeSight.
Powered by
![]()
You need to be a member of MedTech I.Q. to add comments!
Join MedTech I.Q.